US
US
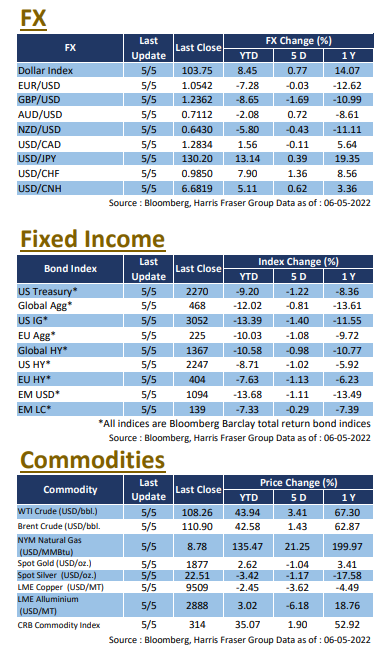
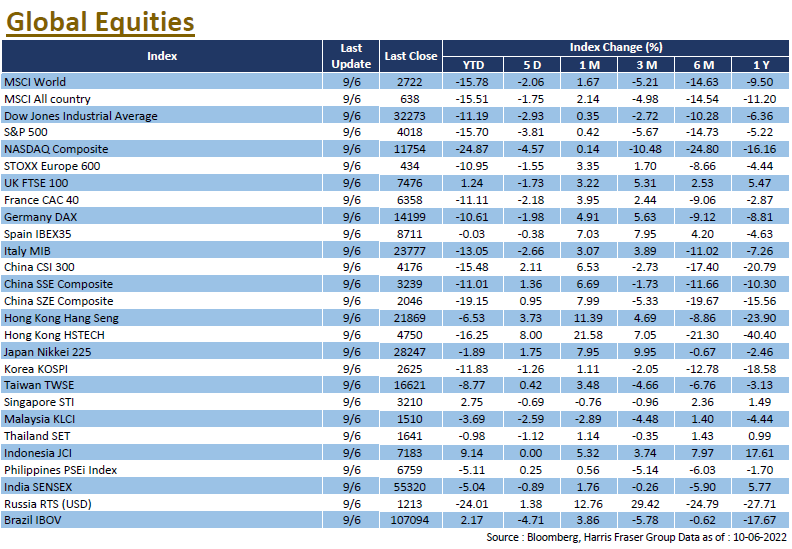
The World Bank and the OECD both lowered their global economic forecasts, together with the ECB signalling a tighter policy on Thursday, US markets fell alongside European equities. Over the past five days ending Thursday, the three major US indices fell between 2.93% and 4.57%. According to a report released by the World Bank, the Russian invasion of Ukraine triggered supply chain disruptions, sending energy and food prices higher, while global central banks raising rates from very low levels will limit growth. Thus, the Bank lowered the global economic growth forecast to 2.9% this year, down from 4.1% and 3.2% in January and April reports respectively. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has also lowered its global growth forecast for this year from 4.5% to 3%, citing the potential lasting impact of the Russia-Ukraine war on the global economy and warning of the risk of a global food crisis.
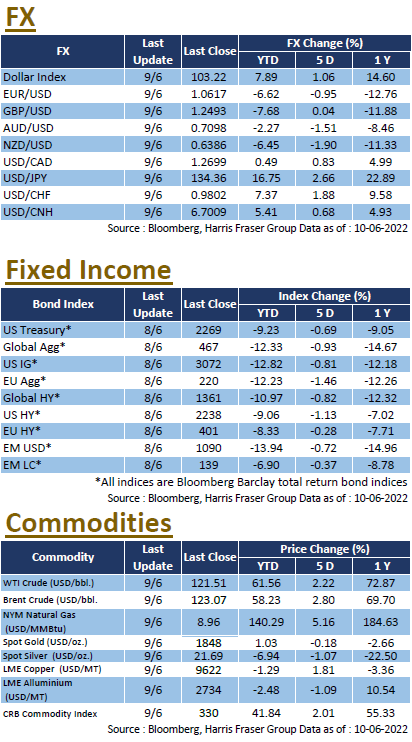
Against the backdrop of high inflation, the Fed is expected to maintain its rapid pace of rate hikes. Alan Blinder, former Vice Chairman of the Federal Reserve, said that a 50 bps rate hike would be needed in each of the next three to four meetings. According to Bloomberg interest rate futures data, the market expects the Fed to raise interest rates by 50 basis points at the June, July, and September meetings. The 10-year US Treasury yield has reached the 3% level once again, while the 2-year yield has also risen to 2.83%, close to its high in early May. Next week, the market will be watching the interest rate meeting on 15 June closely, as well as the US retail sales data.
 Europe
Europe
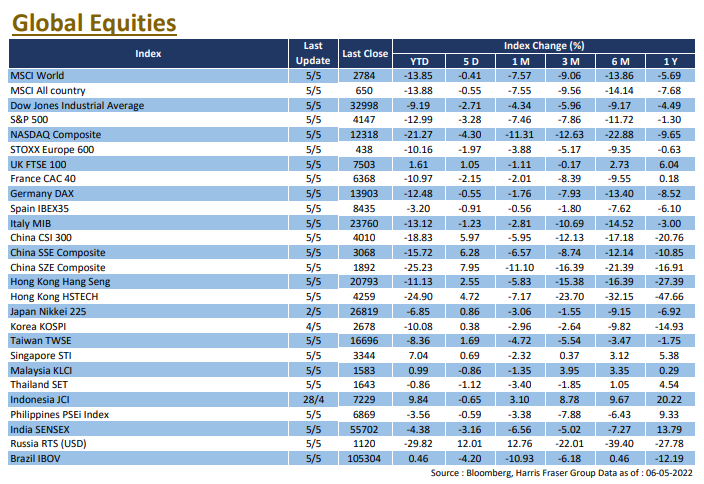
European shares fell after the European Central Bank (ECB) announced that it would end its net bond buying programme, with UK, French, and German equities down 0.75%, 1.96%, and 1.81% respectively over the past five days ending Thursday. The ECB statement noted that the Bank plans to raise interest rates by 25bps in July, and will continue to raise rates in September. If the medium-term inflation outlook remains unchanged or worsens, the rate hike in September could be more substantial. In the UK, incumbent Prime Minister Boris Johnson will remain the leader of the Conservative Party and Prime Minister of the UK after winning a no-confidence vote within his party. Next week, the Bank of England will hold an interest rate meeting and is expected to raise its current interest rate of 1.00% to 1.25%.
 China
China
Supported by various factors such as the epidemic getting under control and the implementation of supportive policies, the Hong Kong and Chinese stock markets remained strong, with the Hang Seng Index gaining 3.43% and the Hang Seng Tech Index surging 9.75% for the week; the China A-share market was equally strong, with the CSI 300 Index rising 3.65% for the week. China's PPI rose at a cooler 6.4% YoY in May, while the CPI remained unchanged at 2.1% YoY over the same period. Aggregate financing and new RMB loans both exceeded market expectations in May, while M2 money supply expanded at a faster pace. The market was also buoyed by a surge in Chinese technology stocks, following reports that the Chinese authorities may end their investigation into DiDi, and that Ants Group was resuming its listing process, which the latter was later debunked. Next week, China will release fixed investment, industrial production, and retail sales figures.




 US
US Europe
Europe China
China